This web page was produced as an assignment for Gen677 at UW-Madison Spring 2010
Phylogeny
A phylogeny tree shows the evolutionary development and history of organisms using genetic sequences, protein sequences, morphology, or a combination of the three with other characteristics. It can determine how gene have evolved through the presence of mutations, deletions, and insertions in a gene.
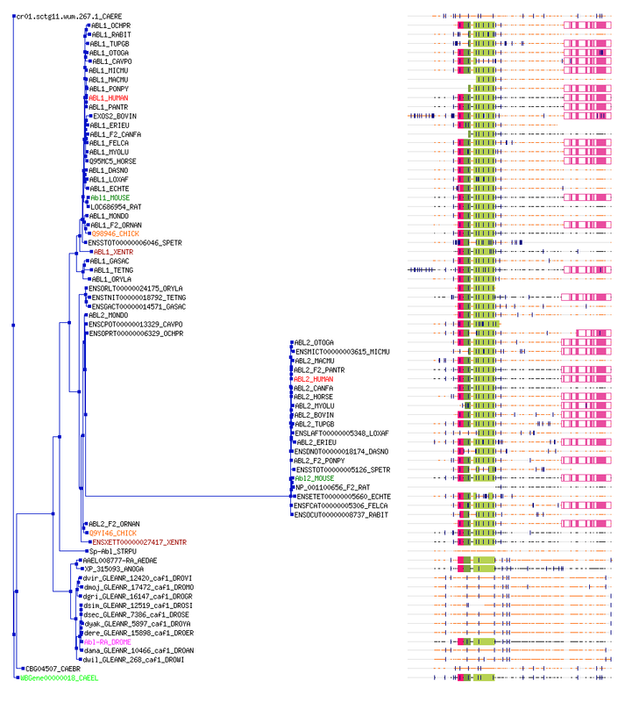
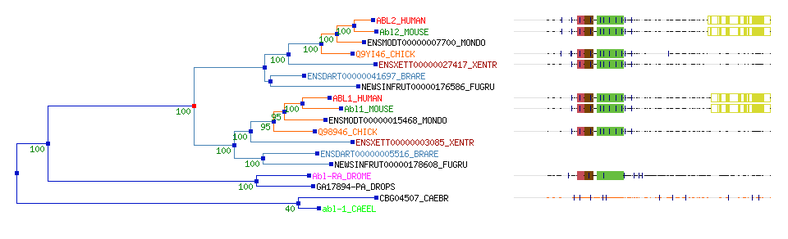
The phylogeny tree using the gene sequence alignment was determined by TreeFam since this was the only program that provided a gene sequence alignment. Below are the automatic clean tree and curated seed tree along with the alignment appearance next to the organism's that have been sequenced for the ABL1 gene. The red node found in the curated seed tree indicates a duplication of the gene.
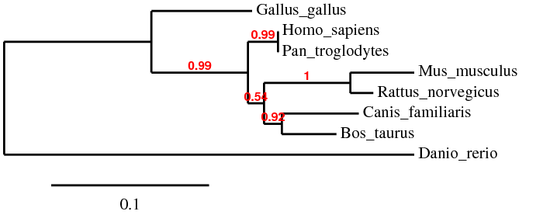
A phylogeny tree was also determined from the protein sequence alignment. Phylogeny.fr was used to form phylogeny trees from the ClusterW, Muscle, and T-Coffee alignments. All three generated similar trees. The only differences were in the branch length and the branch supportative values. Below is the phylogeny tree generated using the T-Coffee alignment.
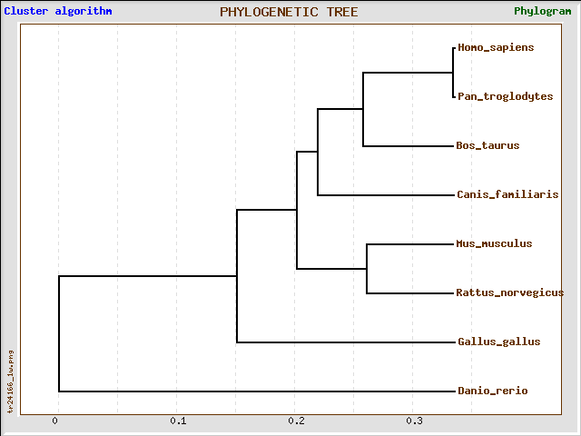
Another phylogeny tree was also generated using the T-Coffee alignment using TreeTop and can be seen below.
Analysis
The phylogeny trees above show a high phylogenetic relationship between mammals specifically the chimpanzee and mouse. The branch lengths also indicate the ABL1 gene evolved within a short time frame of each other for the mammals. The chicken's version of the ABL1 gene evolved earlier than the mammals. It also becomes clearer that the F-actin binding domain evolved in humans and other mammals containing the homolog but not in the chicken. Both also show that C. elegans have a simpler version of the ABL-1 gene called abl-1 that was not found to be a homolog.
The phylogeny trees generated from the protein sequences are very similar to the phylogeny trees generated by the genetic sequence. The trees do disagree in the development and history of the ABL1 gene and protein sequence in the mammals. This provides further evidence of the conservation and of the ABL1 gene between the mammals and indicates the importance of the role of the gene that it needs to be conserved to such a high degree.
The phylogeny trees generated from the protein sequences are very similar to the phylogeny trees generated by the genetic sequence. The trees do disagree in the development and history of the ABL1 gene and protein sequence in the mammals. This provides further evidence of the conservation and of the ABL1 gene between the mammals and indicates the importance of the role of the gene that it needs to be conserved to such a high degree.
References
1. Phylogeny.fr http://www.phylogeny.fr/
2. TreeFam http://www.treefam.org/
3. TreeTop http://www.genebee.msu.su/services/phtree_reduced.html
2. TreeFam http://www.treefam.org/
3. TreeTop http://www.genebee.msu.su/services/phtree_reduced.html